In the intricate dance of economics, few concepts hold as much sway as supply and demand. Understanding the interplay between these two forces is crucial for unraveling the mysteries of markets and pricing. In this comprehensive guide, we embark on a journey to demystify supply and demand, shedding light on their mechanisms and implications. Whether you’re a seasoned economist or a curious learner, join us as we delve into the heart of economic theory.
The Foundation of Economics
At its core, economics revolves around the simple yet profound relationship between supply and demand. These twin pillars dictate the allocation of resources, shape pricing decisions, and influence market behavior. Let’s explore each element to lay the groundwork for our understanding.
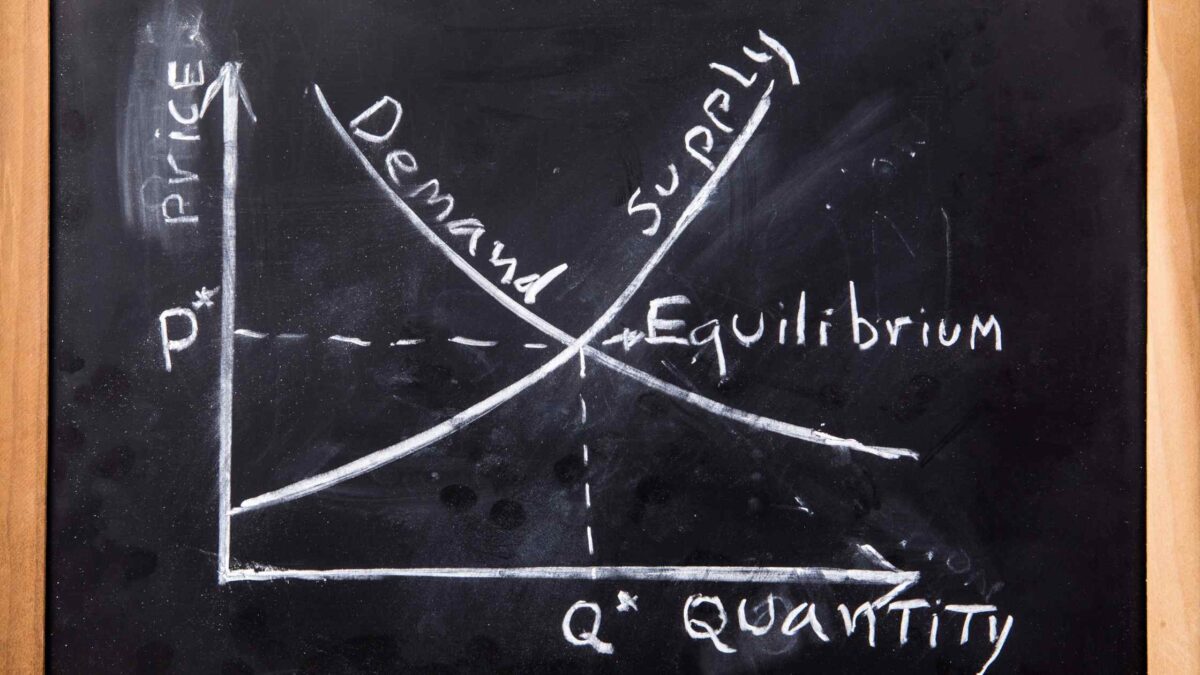
Supply: The Backbone of Markets
Supply embodies the quantity of goods or services that producers can offer for sale at various price levels within a given period. It reflects the producers’ responsiveness to changes in price, production costs, and technological advancements. Understanding the dynamics of supply is essential for predicting how producers will react to shifts in market conditions.
Supply is contingent upon factors such as production costs, technological innovations, and resource availability. As production costs decrease or technological advancements streamline processes, producers can offer more goods at lower prices, expanding the supply curve. Conversely, factors like resource scarcity or regulatory constraints may restrict supply, causing the curve to contract.
Demand: The Engine of Consumption
On the other side of the equation lies demand, representing the desire and ability of consumers to purchase goods and services at various price levels within a given period. Demand reflects consumers’ preferences, income levels, and the availability of substitute goods. Analyzing demand patterns is crucial for understanding consumer behavior and forecasting market trends.
Demand is influenced by a myriad of factors, including price levels, consumer preferences, and income distribution. When prices decrease, the quantity demanded typically increases, following the law of demand. Conversely, rising prices may deter consumers, leading to a decrease in demand. Understanding these dynamics is key for businesses to devise effective pricing strategies and optimize their market positioning.
Market Equilibrium: Where Supply Meets Demand
At the intersection of supply and demand lies market equilibrium, the point at which the quantity supplied equals the quantity demanded at a given price level. Market equilibrium signals a state of balance, where neither surpluses nor shortages exist. Understanding this equilibrium point is crucial for gauging market stability and predicting price fluctuations.
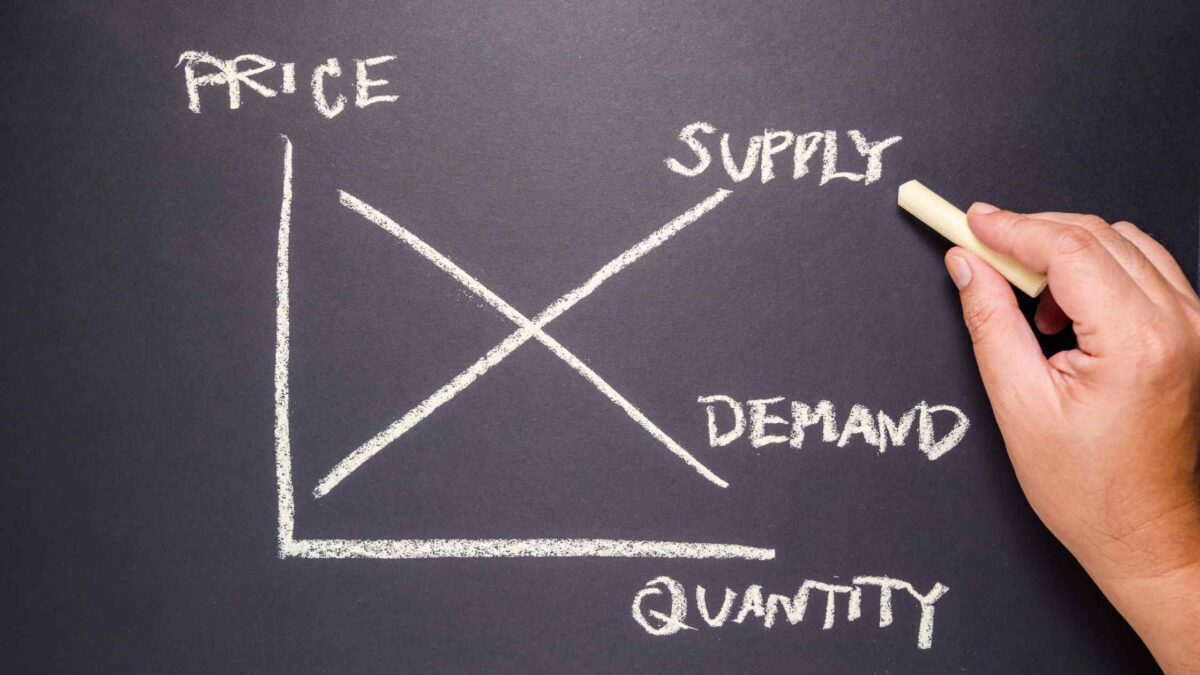
Market equilibrium serves as a guiding principle for pricing decisions and resource allocation. When supply exceeds demand, prices tend to decrease, signaling producers to reduce output or innovate to align with consumer preferences. Conversely, when demand outstrips supply, prices rise, incentivizing producers to increase output and capitalize on market opportunities.
The Dynamics of Supply and Demand
Having laid the groundwork, let’s delve deeper into the intricate dynamics of supply and demand. By examining real-world examples and case studies, we’ll gain a nuanced understanding of how these forces shape market outcomes and drive economic phenomena.
Elasticity: The Measure of Responsiveness
Elasticity measures the responsiveness of supply and demand to changes in price or other external factors. Understanding elasticity is essential for assessing the sensitivity of market participants to price fluctuations and predicting their behavioral responses.

Pricing Strategies: Maximizing Profits in a Dynamic Environment
In a competitive marketplace, pricing strategies play a pivotal role in determining a firm’s profitability and market share. From cost-plus pricing to dynamic pricing algorithms, businesses employ a variety of tactics to optimize their pricing decisions and gain a competitive edge.
External Factors: Navigating the Economic Landscape
Beyond internal dynamics, external factors exert a significant influence on supply and demand dynamics. From macroeconomic trends to geopolitical events, a myriad of factors can disrupt market equilibrium and reshape consumer behavior. Understanding these external forces is crucial for businesses and policymakers alike to anticipate market shifts and mitigate risks.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
1. What is the role of supply and demand in setting prices?
Supply and demand serve as the fundamental determinants of market prices. When supply exceeds demand, prices tend to decrease, signaling an oversupply. Conversely, when demand outstrips supply, prices rise, reflecting scarcity in the market.
2. How do shifts in supply and demand affect market equilibrium?
Shifts in supply and demand can alter market equilibrium, leading to changes in price levels and quantities exchanged. For example, an increase in demand with constant supply will lead to higher prices and quantities exchanged, while a decrease in supply with constant demand will lead to lower quantities exchanged and higher prices.
3. What factors influence the elasticity of supply and demand?
The elasticity of supply and demand is influenced by various factors, including the availability of substitutes, the necessity of the good or service, time horizons, and income levels. Goods with close substitutes tend to have more elastic demand, while goods with limited substitutes exhibit inelastic demand.
4. How do businesses adapt their pricing strategies in response to changes in supply and demand?
Businesses may adjust their pricing strategies in response to shifts in supply and demand to maximize profitability and maintain market competitiveness. For example, during periods of high demand and limited supply, businesses may implement surge pricing to capture additional revenue.
5. What role do government policies play in regulating supply and demand?
Government policies can have a significant impact on supply and demand dynamics through regulations, subsidies, taxes, and trade policies. For example, price controls may be imposed to mitigate the effects of market imbalances, while subsidies may incentivize the production or consumption of certain goods.
6. How can businesses anticipate and respond to changes in external factors affecting supply and demand?
Businesses can employ market research, data analysis, and scenario planning to anticipate and respond to changes in external factors affecting supply and demand. By staying agile and adaptive, businesses can capitalize on opportunities and mitigate risks in a dynamic economic landscape.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding the intricacies of supply and demand is paramount for navigating the complexities of the modern economy. By grasping the fundamental principles and dynamics at play, businesses, policymakers, and consumers alike can make informed decisions and thrive in a dynamic marketplace. Whether you’re a novice or an expert, the journey to understanding supply and demand is a rewarding one, filled with insights and opportunities for growth.
- 10 Best Essential Business Management Techniques You Need to Know
- Maximize Efficiency and Growth: Expert Product and Service Management Solutions
- Why Macroeconomics is the study of the economy as a whole – Best Info
- Understanding Supply and Demand: A Comprehensive Explanation
- The Nature and Scope of Macroeconomics- A Best Guide

